On December 31, 2024, members of the Westlake Genetech R&D team published a paper entitled “Improved split prime editors enable efficient in vivo genome editing” online in Cell Reports.
To access the paper, please visit: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115144.
Background
Prime Editing (PE) is a CRISPR/Cas-based gene editing tool that enables precise base conversions, insertions, and deletions without inducing DNA double-strand breaks, holding great potential for correcting most known mutations associated with human genetic diseases.
However, the large size of the prime editor exceeds the packaging capacity of a single AAV (4.7 kb), requiring delivery via a dual-AAV system.
This approach, known as split-PE, involves splitting the PE-encoding sequence into two fragments, which are delivered into the cells via dual AAVs and reassembled into functional PE through trans-splicing.
A key challenge in the field has been identifying optimal split sites to maximize the in vivo editing efficiency of split-PE.
Research Findings
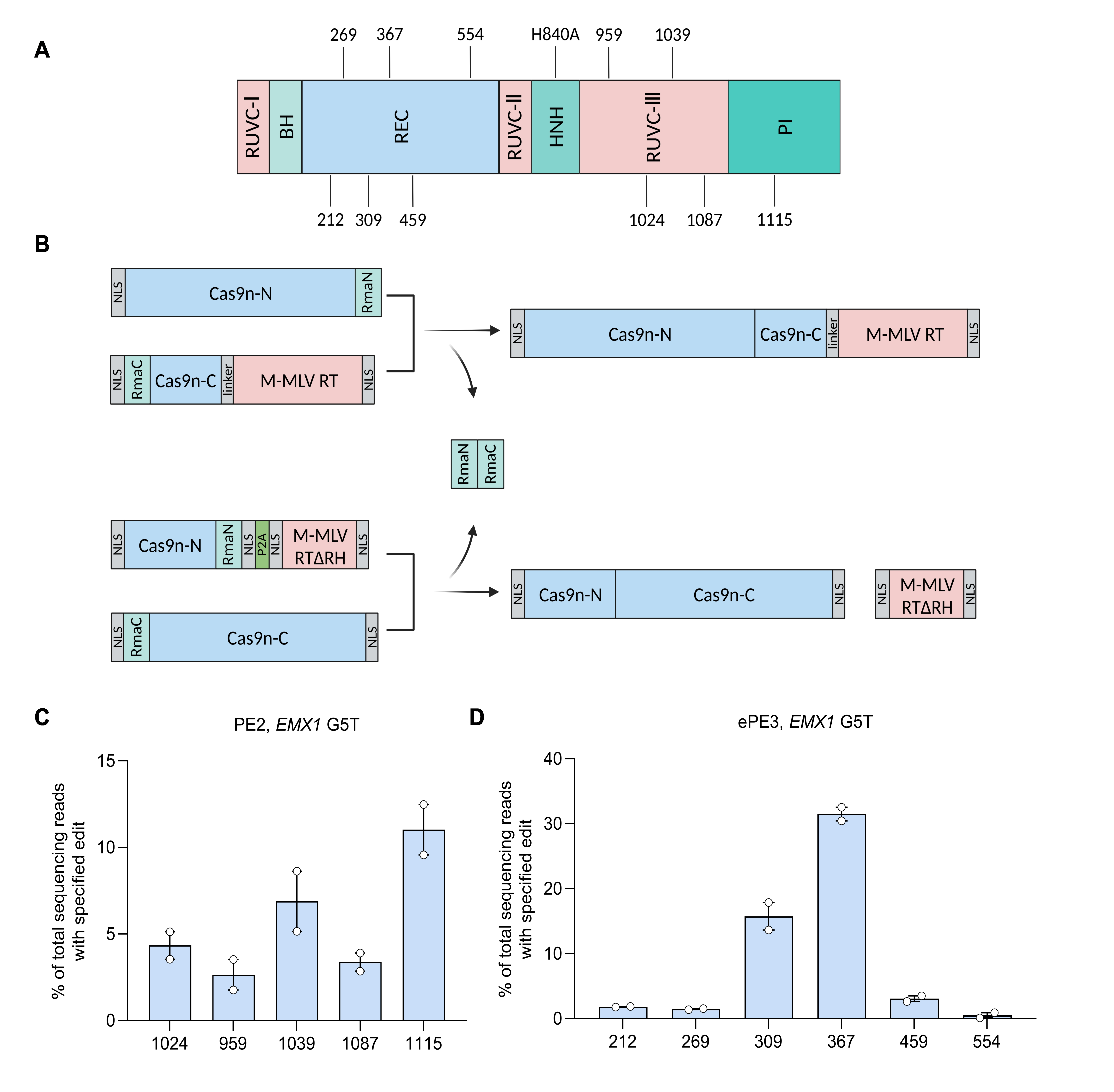
This study identified efficient split sites for split-PE (Fig. 1A), designed a novel PE architecture, and achieved efficient in vivo genome editing via dual-AAV delivery of PE.
• Efficient Split Sites Screening: The team tested multiple split sites in vitro and identified split-PE-1115 as highly efficient (Fig. 1B-C). Additionally, using untethered reverse transcriptase (RT), they screened split sites near the N-terminus of Cas9 nickase (Cas9n) and validated split-PE-367 as another high-performance variant (Fig. 1B, D). Both split-PE-1115 and split-PE-367 demonstrated superior editing efficiency compared to existing split-PE systems across multiple genomic loci.
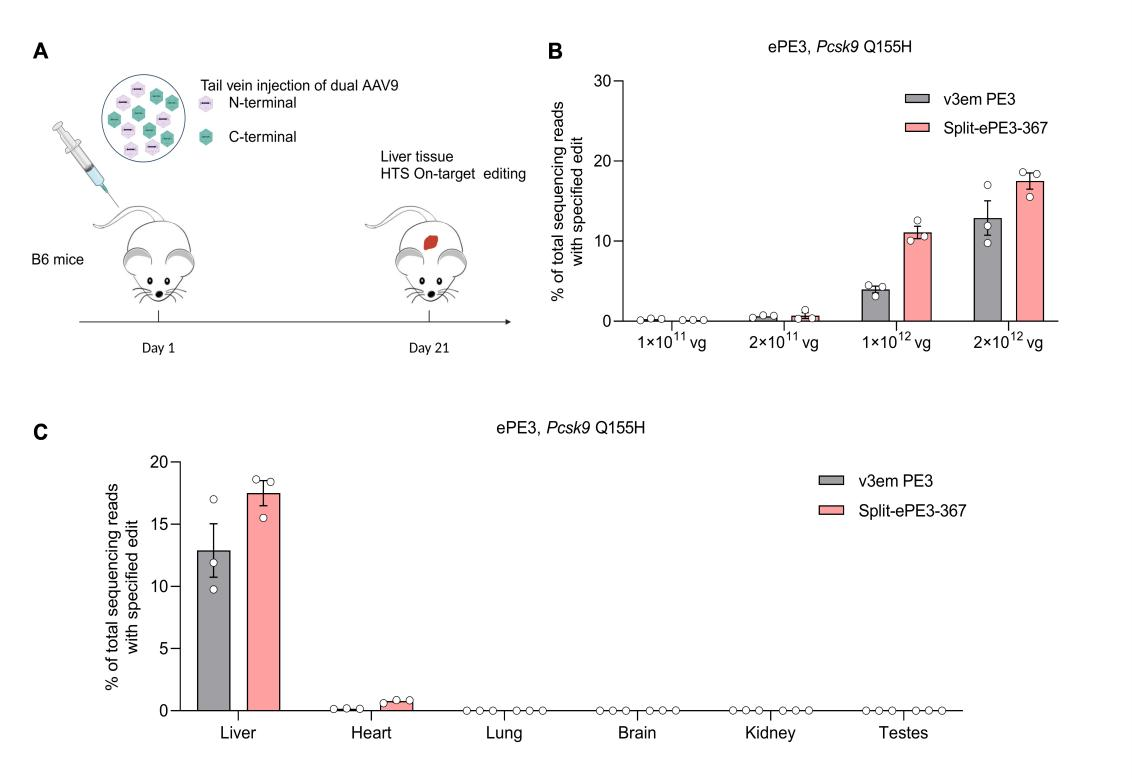
• In Vivo Validation: split-ePE3-367 was packaged into AAV9 and used to target the PCSK9 gene (a key regulator of cholesterol homeostasis) in mice (Fig. 2A). The results showed precise editing of PCSK9 Q155H with a maximum efficiency of 17.5%—outperforming the previously reported optimal strategy (12.9%) (Fig. 2B-C). No significant off-target editing was detected, confirming excellent safety.
Conclusion
By utilizing untethered RT, this study expanded the screening window for split sites and identified highly efficient variants (e.g., split-PE-367).
By using AAV, the split-ePE3-367 enables efficient, specific in vivo gene editing in mice, demonstrating the potential of dual-AAV-delivered split-ePE3-367 for treating genetic diseases.
Future work will focus on exploring additional efficient split sites and evaluating the efficiency and accuracy of the new split-PE system for editing genes associated with various diseases.
About Westlake Genetech
Westlake Genetech is an innovative biotech company focused on leveraging AI to accelerate the research and development of next-generation gene therapies.
Through the proprietary gene therapy technology platforms, the company has achieved significant technological breakthroughs in capsid engineering and payload redesigning, including novel AAV variants with tropism for T cells, CNS and muscle tissues, as well as optimized gene-editing tools.
These innovations will help drive the development of safer, more accessible and more efficient gene therapies to address more unmet needs.
Contacts: bd@westlakegenetech.com

| bd@westlakegenetech.com | |
| 浙江省杭州市西湖区转塘街道云梦路1号1幢6楼 |

